Biome mapping across North America unveils the continent’s ecological tapestry, providing a comprehensive understanding of the distribution, patterns, and significance of its diverse ecosystems. By employing various mapping techniques, scientists have identified major biomes and their intricate transitions, revealing the complex interplay between climate, topography, and other environmental factors.
This intricate mapping process not only enhances our knowledge of North America’s ecosystems but also serves as a valuable tool for land management, conservation planning, and climate change research. Biome maps empower decision-makers to make informed choices, ensuring the preservation and sustainable use of these vital ecological resources.
Biome Mapping Techniques
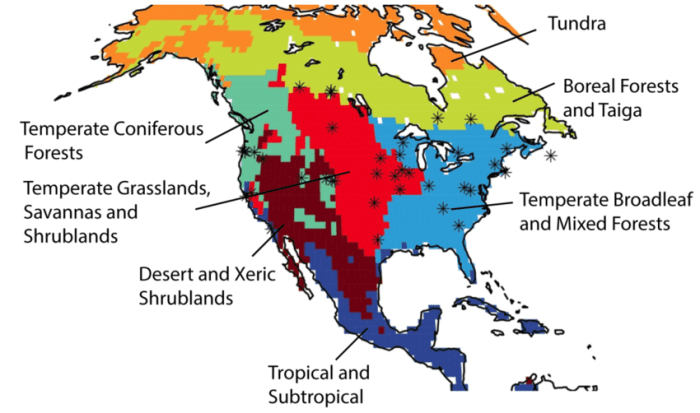
Biome mapping involves identifying and mapping different biomes, which are large-scale ecological communities characterized by distinct plant and animal life. Various methods are used for biome mapping across North America:
Remote Sensing
- Uses satellite imagery and aerial photography to classify land cover and vegetation types, providing a broad overview of biomes.
- Advantages: Wide coverage, cost-effective, and can be automated.
- Disadvantages: May not capture fine-scale variations or changes over time.
Field Surveys
- Involves on-the-ground observations and data collection to identify and map biomes.
- Advantages: Provides detailed and accurate data, can capture fine-scale variations.
- Disadvantages: Time-consuming, expensive, and may not cover large areas.
Modeling
- Uses mathematical models to predict the distribution of biomes based on environmental variables such as climate, soil type, and topography.
- Advantages: Can generate detailed and continuous maps, can predict future changes.
- Disadvantages: Relies on accurate input data, may not capture complex ecological interactions.
Examples of Successful Biome Mapping Projects
- North American Biome Map (NABM): A comprehensive map of biomes across North America using a combination of remote sensing and field surveys.
- Biosphere Reserves Map of North America: Maps the distribution of biosphere reserves, which are protected areas representing major biomes.
- National Land Cover Database (NLCD): Provides detailed land cover data for the United States, which can be used for biome mapping.
Biome Distribution and Patterns: Biome Mapping Across North America
North America is home to a wide range of biomes, each with its unique characteristics:
Major Biomes of North America
- Tundra: Cold, treeless regions with permafrost.
- Boreal Forest: Coniferous forests with cold winters and moderate summers.
- Temperate Forest: Deciduous forests with warm summers and cool winters.
- Grassland: Open, grassy areas with moderate rainfall.
- Desert: Arid regions with sparse vegetation.
- Mediterranean: Coastal regions with mild winters and hot, dry summers.
Distribution and Patterns
- Tundra and Boreal Forest dominate the northern regions of North America.
- Temperate Forest covers much of the eastern United States and Canada.
- Grasslands occur in the central plains and western United States.
- Deserts are found in the southwestern United States and Mexico.
- Mediterranean climate is present in California and parts of Chile.
Factors Influencing Biome Distribution
- Climate: Temperature, precipitation, and seasonality.
- Topography: Elevation, slope, and aspect.
- Soil Type: Fertility, texture, and drainage.
- Disturbance: Natural events (e.g., fire, hurricanes) and human activities.
Biome Transitions and Ecotones
Biome transitions occur where two or more biomes meet. Ecotones are the transitional zones between biomes, which exhibit characteristics of both adjacent biomes.
Major Biome Transitions in North America
- Tundra-Boreal Forest
- Boreal Forest-Temperate Forest
- Temperate Forest-Grassland
- Grassland-Desert
- Desert-Mediterranean
Ecological Significance of Ecotones
- High biodiversity due to the presence of species from both adjacent biomes.
- Provide important habitat for migratory species.
- Buffer zones between different biomes, reducing the impact of disturbances.
Applications of Biome Mapping
Biome mapping is used in various applications:
Land Management
- Identify areas for conservation and protection.
- Plan for sustainable land use practices.
- Monitor changes in land cover and vegetation.
Conservation Planning
- Prioritize areas for conservation based on biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Identify threatened and endangered species habitats.
- Design wildlife corridors and protected areas.
Climate Change Research, Biome mapping across north america
- Monitor changes in biome distribution over time.
- Predict future shifts in biomes due to climate change.
- Identify vulnerable ecosystems and species.
Benefits and Limitations of Biome Maps
- Benefits: Provide a comprehensive overview of biomes, support decision-making, and monitor environmental changes.
- Limitations: May not capture fine-scale variations, may be outdated over time, and may not consider ecological processes.
Quick FAQs
What are the primary methods used for biome mapping across North America?
Biome mapping techniques include remote sensing, field surveys, and vegetation analysis, each with its advantages and limitations.
How do climate and topography influence biome distribution in North America?
Climate factors such as temperature, precipitation, and sunlight determine the suitability of an area for a particular biome, while topography affects local climate patterns and creates microclimates that support diverse plant and animal communities.
What is the ecological significance of ecotones in North America?
Ecotones, transition zones between different biomes, serve as areas of high biodiversity and ecological productivity, supporting a wide range of species that rely on the resources of both adjacent biomes.