The Three Branches of Government Graphic Organizer presents a comprehensive overview of the intricate system of checks and balances that underpins democratic societies. This guide delves into the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, exploring their distinct roles, structures, and the essential principles that ensure no one branch becomes overly powerful.
The legislative branch, responsible for creating laws, is examined in detail, highlighting its composition, organization, and the processes involved in lawmaking. The executive branch, tasked with enforcing laws, is analyzed, with emphasis on its structure, leadership, and the mechanisms through which it executes its authority.
The Three Branches of Government: Three Branches Of Government Graphic Organizer
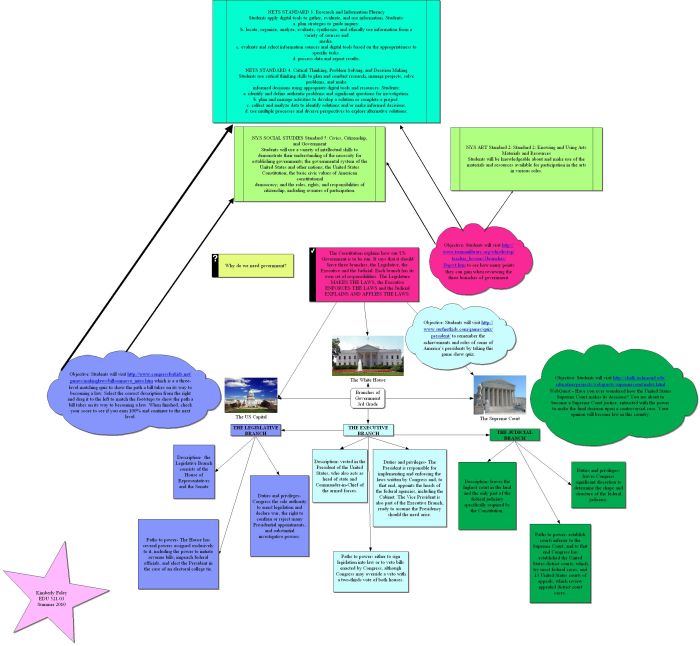
The concept of the three branches of government is a fundamental principle in democratic societies. It involves the separation of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. This division of authority ensures that no single entity can become too powerful and that the rights of citizens are protected.The
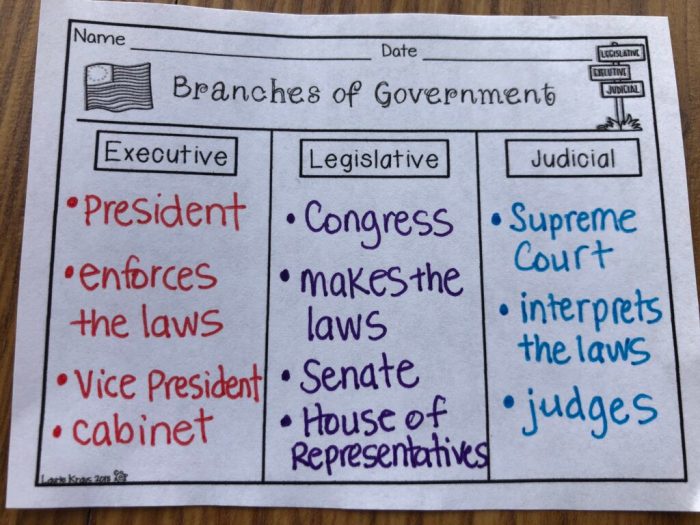
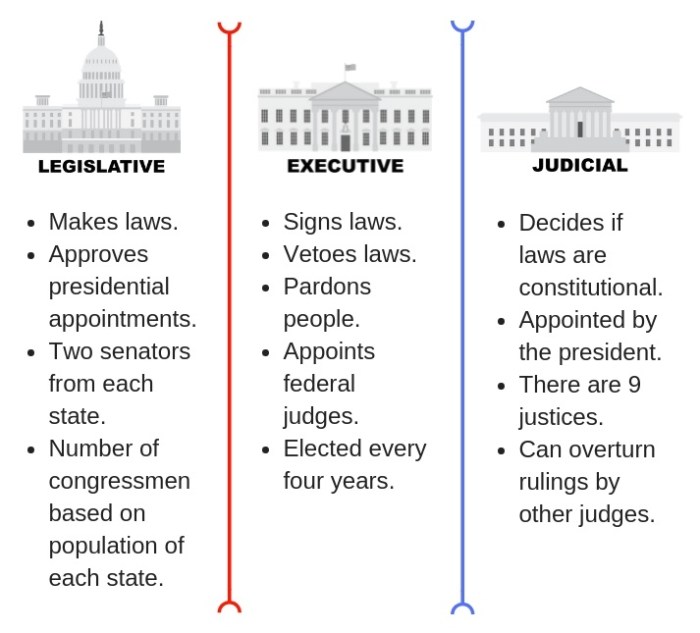
legislative branch is responsible for creating laws. It is typically composed of a parliament or congress, which is elected by the people. The legislative branch has the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. It also has the power to oversee the executive branch and to impeach the president or other high-ranking officials.The
executive branch is responsible for enforcing laws. It is typically headed by a president or prime minister, who is elected by the people or chosen by the legislature. The executive branch has the power to appoint cabinet members and other officials, to negotiate treaties, and to command the armed forces.The
judicial branch is responsible for interpreting laws. It is typically composed of a supreme court and lower courts. The judicial branch has the power to review laws and to declare them unconstitutional. It also has the power to resolve disputes between individuals and organizations.The
system of checks and balances is a key feature of the three branches of government. This system prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful. For example, the legislature can pass laws, but the president can veto them. The judiciary can declare laws unconstitutional, but the legislature can override those decisions with a two-thirds vote.
Key Questions Answered
What is the primary function of the legislative branch?
The legislative branch is responsible for creating laws that govern society.
How does the executive branch enforce laws?
The executive branch, led by the president, is responsible for implementing and enforcing laws passed by the legislative branch.
What is the role of the judicial branch?
The judicial branch interprets laws and ensures their fair and impartial application.