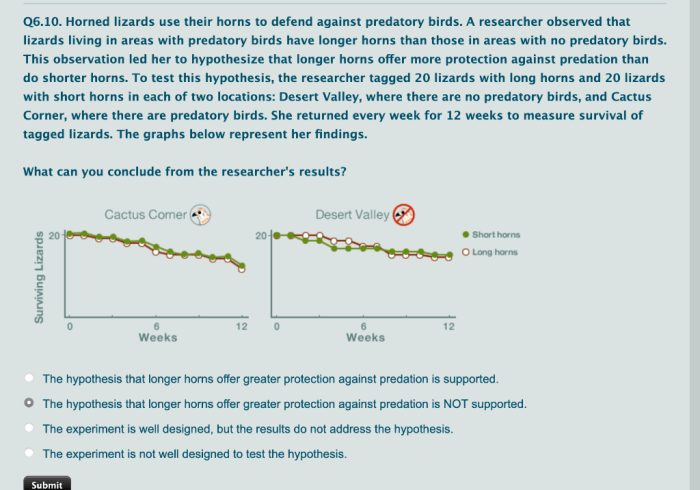
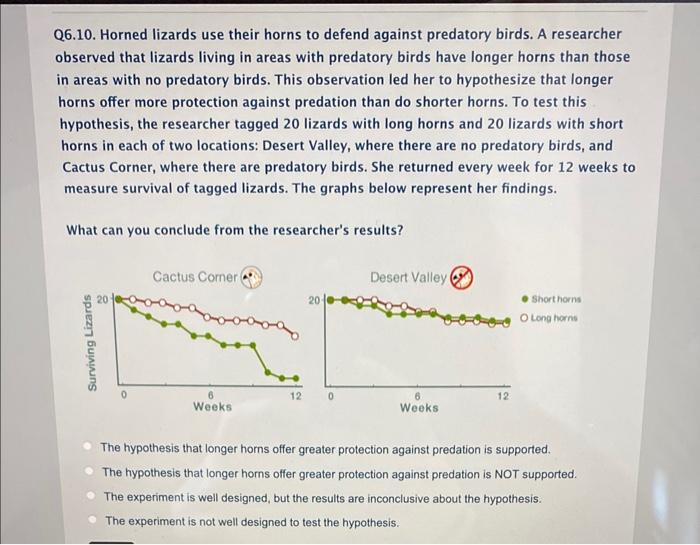
Horned lizards use their horns to defend – Horned lizards, renowned for their distinctive physical attributes, employ their horns as a primary defense mechanism against predators. These horns, strategically positioned on the lizard’s head, play a crucial role in safeguarding the animal from harm.
The significance of horns in the animal kingdom extends beyond defense, serving various purposes such as courtship, territorial displays, and social dominance. However, for horned lizards, the primary function of their horns lies in protection.
Introduction
Horned lizards, renowned for their distinct physical attributes, possess prominent horns that play a significant role in their defense mechanisms. Horns, a prevalent feature in the animal kingdom, serve various purposes, including defense against predators and intraspecific interactions.
Horns provide horned lizards with an effective means of protection, allowing them to fend off potential threats and increase their chances of survival.
Defense Mechanisms

Horned lizards primarily utilize their horns as a defense mechanism against predators. When threatened, they employ various defensive strategies, such as:
- Horn Display:Horned lizards will display their horns by flaring them out and pointing them towards the perceived threat. This display serves as a warning to potential predators, signaling their readiness to defend themselves.
- Horn Thrusting:If a predator persists, horned lizards may resort to thrusting their horns directly at the attacker. This forceful movement can inflict pain and deter the predator from pursuing further.
- Immobility:Horned lizards have the ability to remain motionless for extended periods, relying on their horns and cryptic coloration for protection. This immobility makes them difficult for predators to detect and capture.
Horn Morphology, Horned lizards use their horns to defend
The horns of horned lizards exhibit a remarkable diversity in shape, size, and orientation, contributing to their effectiveness as a defensive mechanism:
- Shape:Horned lizards possess horns that vary in shape, ranging from short and conical to elongated and pointed. The specific shape of the horns is adapted to their defensive strategies.
- Size:The size of the horns is proportional to the size of the lizard. Larger species tend to have more prominent horns, providing them with a greater degree of protection.
- Orientation:Horns are typically located on the head of the lizard, either above or behind the eyes. Their orientation allows for maximum visibility and maneuverability during defensive encounters.
Evolutionary Adaptations

The evolution of horns in horned lizards is a testament to the power of natural selection. Horns have provided a selective advantage, enhancing the survival and reproductive success of these lizards:
- Predator Avoidance:Horns have played a crucial role in reducing predation rates. By deterring predators, horned lizards increase their chances of survival and reaching reproductive maturity.
- Mating Success:In some horned lizard species, males with larger horns are more likely to attract females and secure mating opportunities.
Behavioral Adaptations
Horned lizards exhibit a range of behavioral adaptations that complement their horn defense, further enhancing their ability to survive and reproduce:
- Camouflage:Horned lizards often rely on camouflage to blend in with their surroundings, making them less visible to predators.
- Immobility:As mentioned earlier, horned lizards can remain motionless for extended periods, reducing their detectability.
- Warning Displays:Some horned lizard species engage in warning displays, such as tail-waving or head-bobbing, to deter potential threats.
Clarifying Questions: Horned Lizards Use Their Horns To Defend
How do horned lizards use their horns to defend themselves?
Horned lizards use their horns primarily to deter and ward off predators. When threatened, they will spread their horns, puff up their bodies, and display a threatening posture to intimidate the attacker.
Are the horns of horned lizards sharp?
No, the horns of horned lizards are not sharp. They are made of keratin, the same material that makes up human fingernails, and are primarily used for display and defense rather than inflicting physical harm.