The Cleft Lip and Palate HESI Case Study delves into the complexities of this congenital anomaly, offering a comprehensive overview for nursing professionals. This multifaceted condition presents unique challenges in medical and nursing management, demanding a holistic approach that addresses the physical, psychological, and social well-being of affected individuals and their families.
This case study provides an in-depth exploration of the epidemiology, etiology, clinical presentation, medical and nursing management strategies, and psychosocial impact of cleft lip and palate. By integrating theoretical knowledge with real-world case scenarios, it equips nurses with the essential skills and understanding to provide compassionate and evidence-based care.
Epidemiology
Cleft lip and palate are among the most common birth defects, affecting approximately 1 in 700 live births worldwide.
The prevalence of cleft lip and palate varies among different populations and geographic regions. In the United States, the prevalence is approximately 1 in 1,000 live births, while in some Asian countries, the prevalence can be as high as 1 in 500 live births.
Risk factors for cleft lip and palate include:
- Family history of cleft lip and palate
- Certain genetic syndromes, such as Down syndrome and Pierre Robin sequence
- Maternal smoking during pregnancy
- Maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy
- Maternal use of certain medications, such as anticonvulsants and retinoids
Etiology
The exact cause of cleft lip and palate is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of cleft lip and palate. Several genes have been identified that are associated with an increased risk of cleft lip and palate. However, most cases of cleft lip and palate are not caused by a single gene mutation.
Environmental factors also play a role in the development of cleft lip and palate. Maternal smoking during pregnancy is one of the most well-established environmental risk factors for cleft lip and palate. Other environmental risk factors include maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy, maternal use of certain medications, and exposure to certain chemicals.
Folic acid deficiency has also been linked to an increased risk of cleft lip and palate. Folic acid is a B vitamin that is essential for the proper development of the neural tube. Women who are pregnant or planning to become pregnant should take a folic acid supplement to reduce the risk of neural tube defects, including cleft lip and palate.
Clinical Presentation

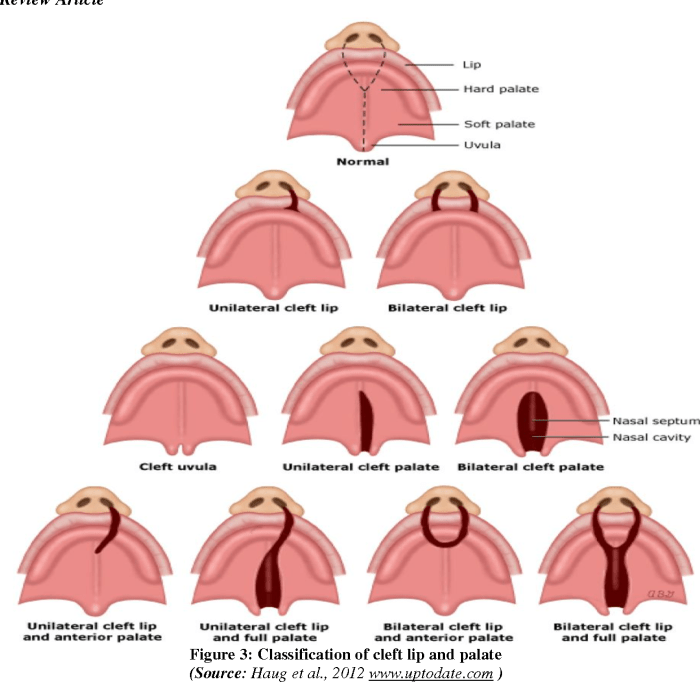
Cleft lip and palate can range in severity from a small notch in the lip to a complete cleft that extends through the lip and palate.
The different types of cleft lip and palate include:
- Cleft lip only
- Cleft palate only
- Unilateral cleft lip and palate
- Bilateral cleft lip and palate
Cleft lip and palate can be associated with a number of other anomalies, including:
- Dental anomalies
- Speech difficulties
- Hearing loss
- Feeding difficulties
- Facial asymmetry
Medical Management
The treatment for cleft lip and palate depends on the severity of the cleft.
Surgical repair is the primary treatment for cleft lip and palate. The goal of surgery is to close the cleft and restore normal function to the lip and palate.
The timing of surgical repair varies depending on the severity of the cleft. Cleft lip is typically repaired within the first few months of life, while cleft palate is typically repaired between 6 and 12 months of age.
In addition to surgery, other treatments for cleft lip and palate may include:
- Speech therapy
- Hearing aids
- Orthodontic treatment
- Psychological support
Nursing Management
The role of the nurse in the care of patients with cleft lip and palate is to provide support and education to the patient and family.
Nurses can play a key role in managing the feeding, speech, and hearing difficulties that are associated with cleft lip and palate.
Nurses can also provide support to the patient and family during the surgical repair process.
Psychosocial Impact
Cleft lip and palate can have a significant psychosocial impact on patients and their families.
Patients with cleft lip and palate may experience teasing and bullying from peers.
Families of patients with cleft lip and palate may experience stress and anxiety related to the child’s condition.
There are a number of support and resources available to patients and families affected by cleft lip and palate.
These resources can provide information, support, and advocacy for patients and families.
Questions Often Asked: Cleft Lip And Palate Hesi Case Study
What are the common risk factors associated with cleft lip and palate?
Risk factors include genetic predisposition, folic acid deficiency, maternal smoking, alcohol consumption, and certain medications.
How does the type of cleft lip and palate affect the treatment plan?
The type of cleft determines the surgical approach and timing of repair, as well as the need for additional interventions such as speech therapy or orthodontics.
What is the role of the nurse in managing feeding difficulties in patients with cleft lip and palate?
Nurses provide support and guidance on feeding techniques, monitor nutritional status, and collaborate with speech therapists to address feeding challenges.
